Track types
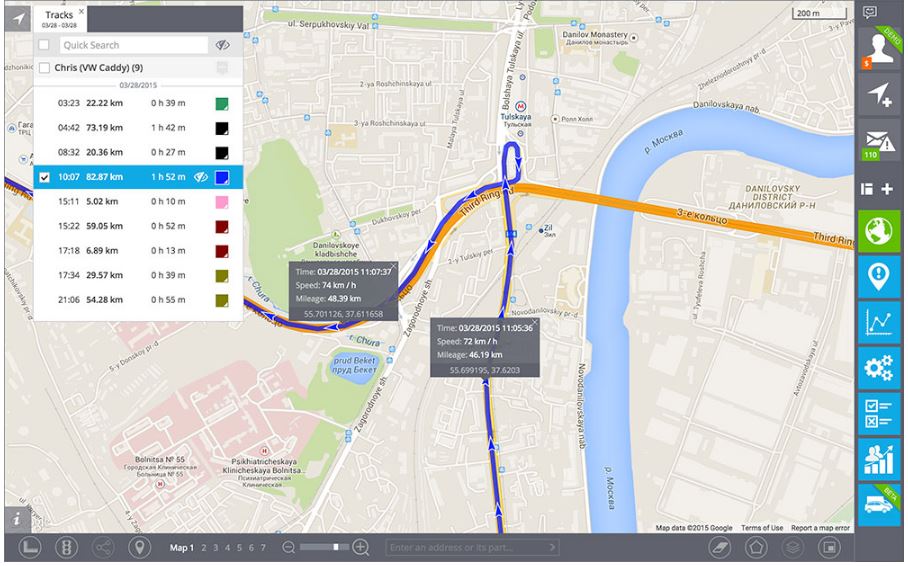
- Continuous tracks. These are the most common tracks, which are very typical for vehicle tracking applications. These tracks are represented as polynomic lines with Start and End.
- Interval tracks. For autonomous GPS trackers it is often set that location is updated in relatively long time intervals, i.e. once per hour, once per day, etc. These tracks will be showed as numbered (1, 2? N) landmarks. For better understanding they will be connected with transparent grey lines, which, however, have little common with real path.
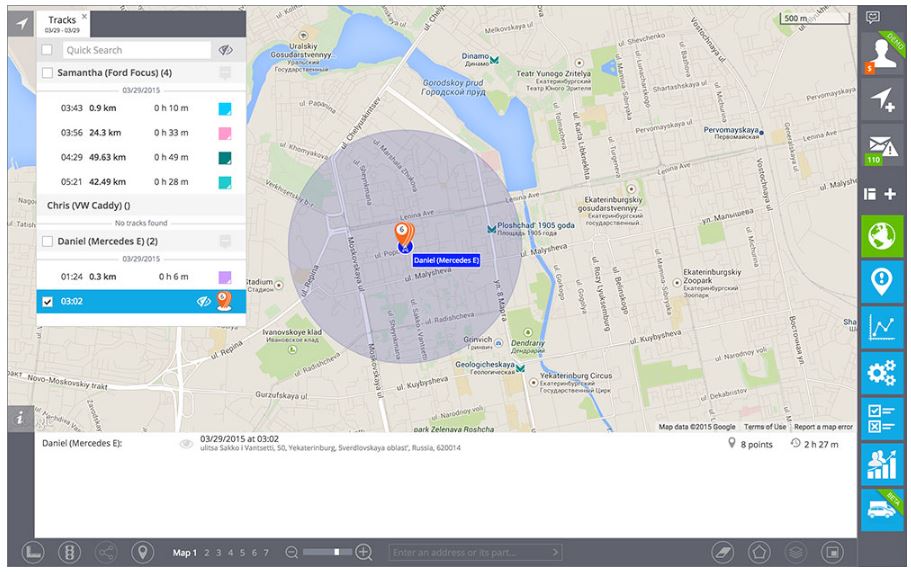
- LBS locations. If location is defined not with satellite navigation systems (GPS, GLONASS, Galileo and others), but with some alternative LBS technologies, such as GSM or Wi-Fi signals, it?s often not very precise. To make it clear to observer, such locations are visualised with circle, which radius means the accuracy.
- Clustered landmarks. When some asset stays in same place too long, you can get too many separate interval orLBS messages for the same locations. To make it more convenient to observer, the server will ?stick? them together and show just one clustered landmark on the map. Start/end time and duration will be added to the note to this landmark.